Common failures of shock absorbers

Shock absorbers soften the impacts and vibrations that occur when a vehicle moves over uneven surfaces and ensure the stability of the vehicle on the road. Failure or degradation of shock absorber performance significantly increases the likelihood of accidents and greatly reduces driving comfort. Let’s look at the most common car shock absorber malfunctions and their possible causes.
1. OIL LEAKS
One of the most common malfunctions is the loss of shock absorber seal integrity. Shock absorbers contain hydraulic fluid, which, in conjunction with valves, provides damping properties. If the shock absorber seals wear out, oil begins to leak, leading to a reduction in damping properties. This manifests as increased vehicle oscillations after passing over bumps, deteriorated handling, and decreased ride comfort.
Main causes of oil leaks:
- Seal wear due to age (high vehicle mileage);
- Installation of the shock absorber with misalignment, causing increased wear;
- Defects on the surface of the rod can damage the shock absorber's oil seal;
- Use of low-quality parts during shock absorber repair.
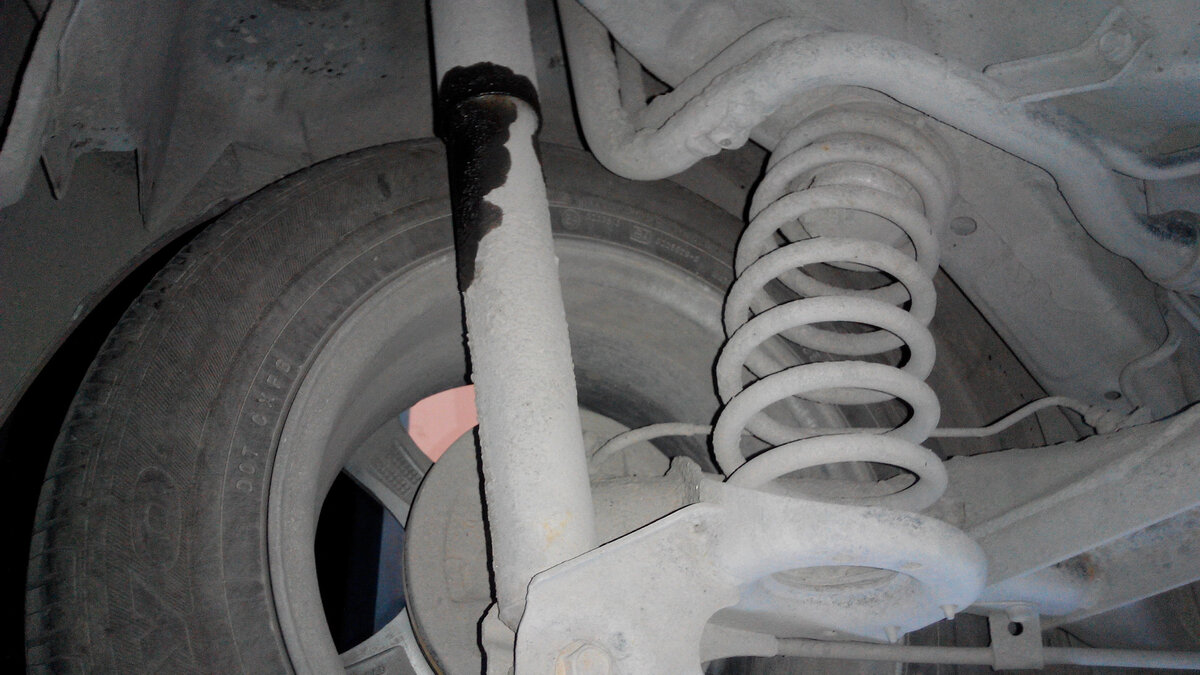

2. FOREIGN NOISES
Another common problem is foreign noises that may come from the shock absorbers. These noises can occur when driving over rough surfaces and often indicate internal damage to the shock absorber or wear of its components.
Causes of foreign noises:
- Wear of bushings and silent blocks;
- Loosening of fastening elements;
- Damage to the rebound and compression valves.
3. LOSS OF DAMPING PROPERTIES
Over time, shock absorbers lose their damping properties, leading to reduced vehicle handling. The car begins to "float" on the road, body roll increases during turns, and road grip deteriorates. This can be especially dangerous at high speeds, as the vehicle becomes less stable.
Causes of loss of damping properties:
- Natural wear over time;
- Damage to the rod seal, resulting in oil leakage;
- Damage to the valve mechanism;
- Deformation or damage to the shock absorber body.
4. CORROSION
Shock absorbers, especially in harsh climates, are susceptible to corrosion. Corrosion of metal parts can significantly shorten the lifespan of the shock absorber, leading to premature failure.
Causes of corrosion:
- Frequent contact with water, dirt, and road chemicals;
- Lack of proper vehicle maintenance;
- Poor quality protective coating on the shock absorber parts during production.

5. SHOCK ABSORBER ROD DEFORMATION
A deformed rod disrupts the system’s seal, leading to oil leaks or complete failure of the unit.
Main causes of rod deformation:
- A strong impact, such as hitting a deep pothole at high speed;
- Poor quality materials used in the manufacture of the shock absorber;
- Overloading the vehicle.
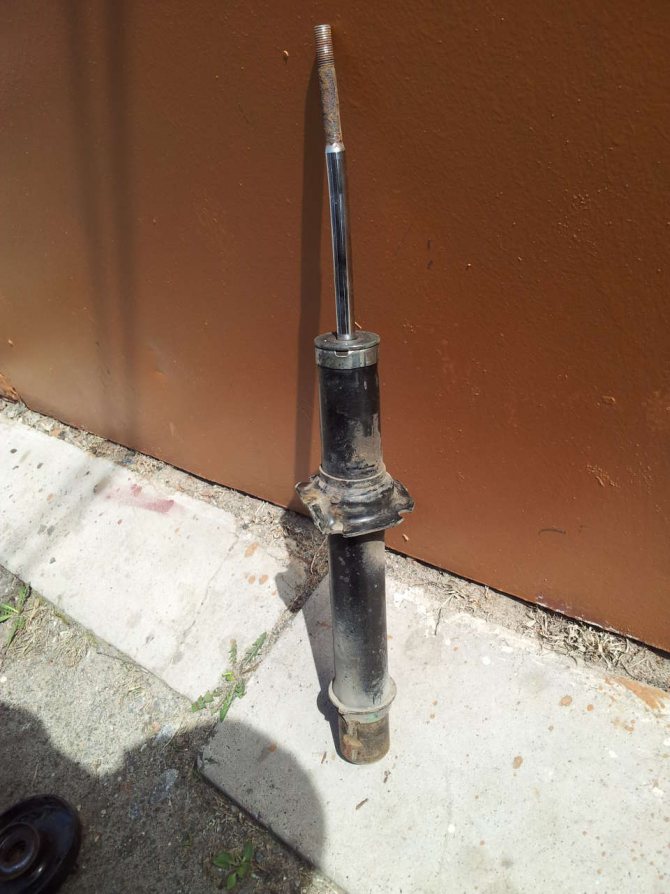

How to diagnose a shock absorber failure
There are many methods for diagnosing shock absorbers, but only two are effective: visual inspection and diagnosis using specialized equipment, such as the MS201 test stand.
The first and simplest method for diagnosing shock absorbers is a visual inspection. This method allows you to identify obvious defects such as oil leaks, corrosion, mechanical damage, and rod or body deformation. However, if a shock absorber shows no external signs of malfunction, this does not mean it is in good condition. To accurately determine the technical condition of the shock absorber, its working diagram (the relationship between resistance force and piston position) must be evaluated at different rod oscillation frequencies.
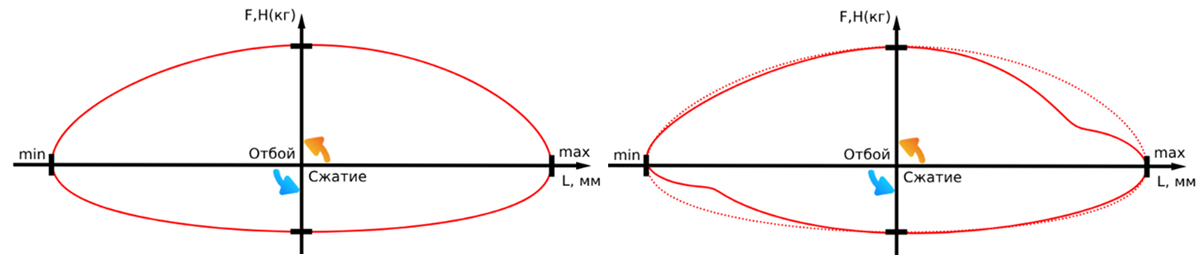
Differences in the working diagram of a functional (left) and malfunctioning (right) shock absorber
The MS201 stand can record the working diagram of a shock absorber with any type of mounting and resistance force on rebound/compression up to 1000 kg. The MS201 stand has the following advantages:
- Diagnosis of electronically controlled shock absorbers with variable stiffness using the MS203 adapter;
- The ability to set the working stroke of the shock absorber;
- Two diagnostic modes: automatic and manual;
- The ability to compare diagnostic results of new and potentially faulty shock absorbers;
- Saving diagnostic results and printing them out;
- Safety of tests for the operator;
- Automatic and free software updates.
Diagnosing car shock absorbers is an important step in ensuring safety and comfort while driving. Therefore, timely detection of shock absorber malfunctions is critically important.







