The automotive industry is constantly evolving, introducing new technologies to enhance the efficiency and environmental friendliness of vehicles. One such innovation is the "mild hybrid" technology (MHEV), which incorporates a 48V starter-generator and a lithium-ion battery. The starter-generator is responsible for engine starting, electricity generation, providing additional torque during rapid acceleration, and energy recuperation during braking. An engine equipped with a starter-generator can be shut off during brief stops, such as at traffic lights, and then restarted within fractions of a second. The "mild hybrid" technology provides 10-15% fuel savings and, most importantly, reduces harmful emissions into the atmosphere.
At present, there are two fundamental designs of starter-generators: the belt-driven starter-generator (BSG) and the integrated starter-generator (ISG). The belt-driven starter-generator is integrated into the Front End Accessory Drive (FEAD) of the engine's additional equipment drive. In this design, the starter-generator replaces the conventional alternator in terms of its role and installation.
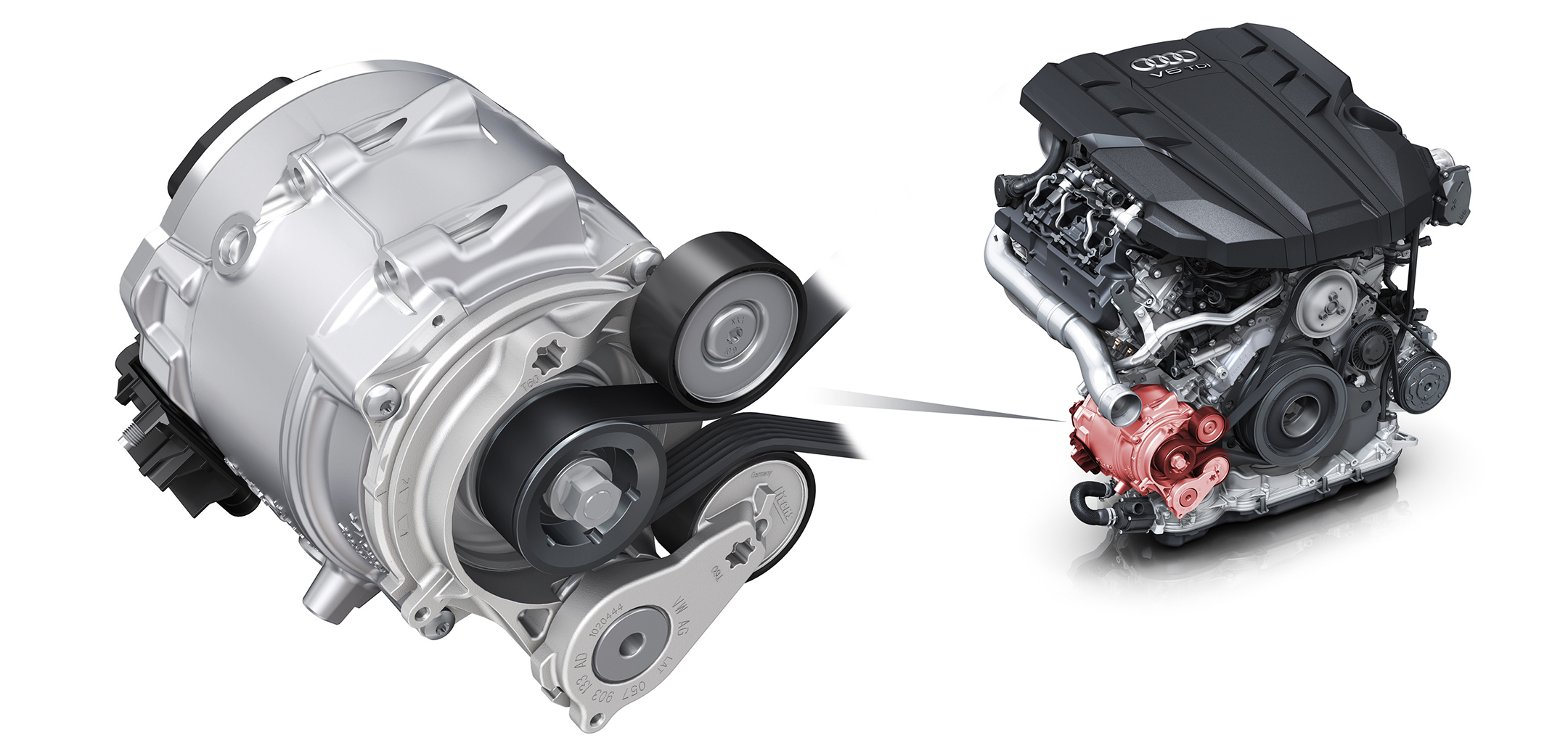
Audi starter-generator belt drive
The integrated starter-generator (ISG) replaces the engine's flywheel, providing higher output power and torque compared to the belt-driven starter-generator. However, installing an integrated starter-generator involves significant engine modifications. Essentially, it results in a completely new engine. Therefore, the belt-driven starter-generator has gained wider acceptance due to its ease of integration into existing engines.
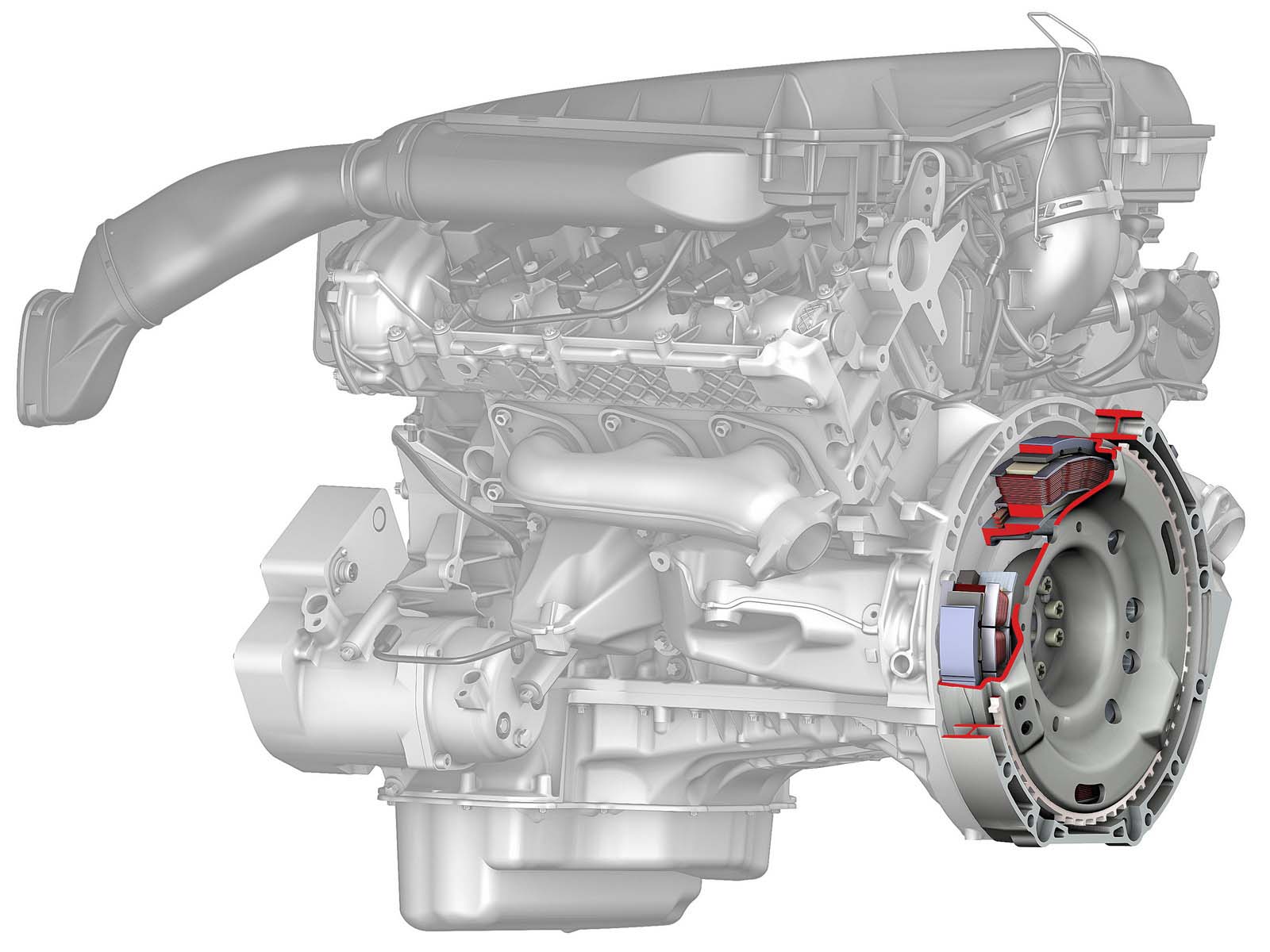
Integrated starter-generator Mercedes-Benz S400 BlueHyrbid
How is the belt starter-generator designed?
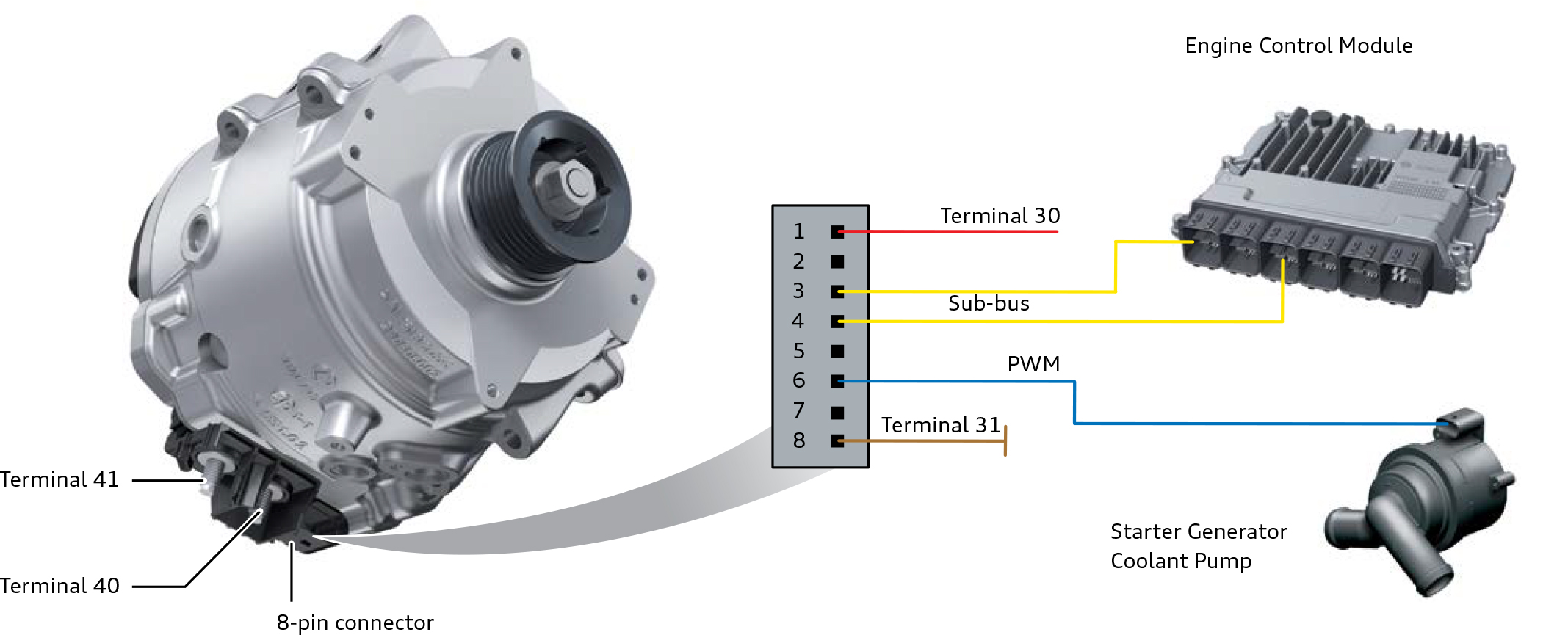
The structure of the belt-driven starter-generator involves a three-phase alternating current (AC) electric motor with a built-in inverter. Depending on the power rating, the starter-generator may have air or liquid cooling.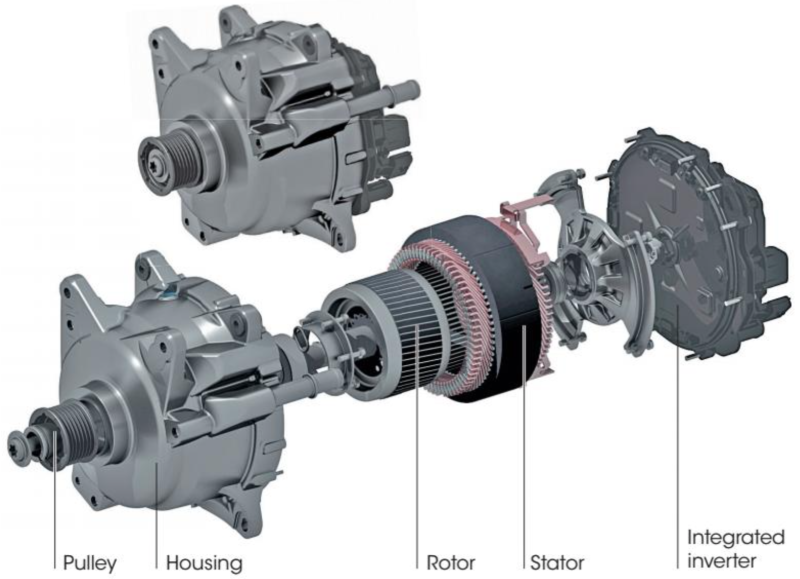
Continental 48 V belt starter-generator design
The belt-driven starter-generator is controlled and exchanges data with the engine control unit via the CAN bus. Additionally, the starter-generator independently controls the coolant pump (in the case of liquid cooling) using pulse-width modulation (PWM) signals.
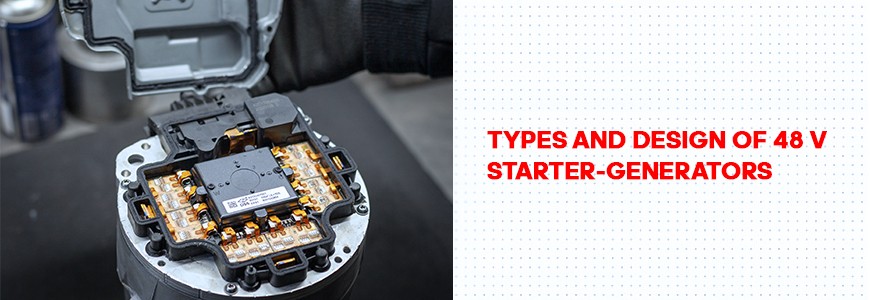
Disassembling a belt-driven starter-generator is a non-trivial and labor-intensive task. Under the single cover on the housing lies the power electronics.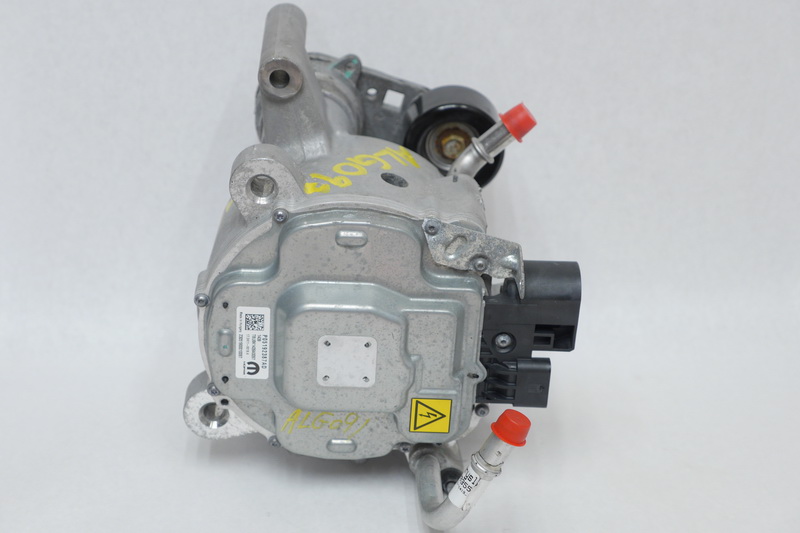
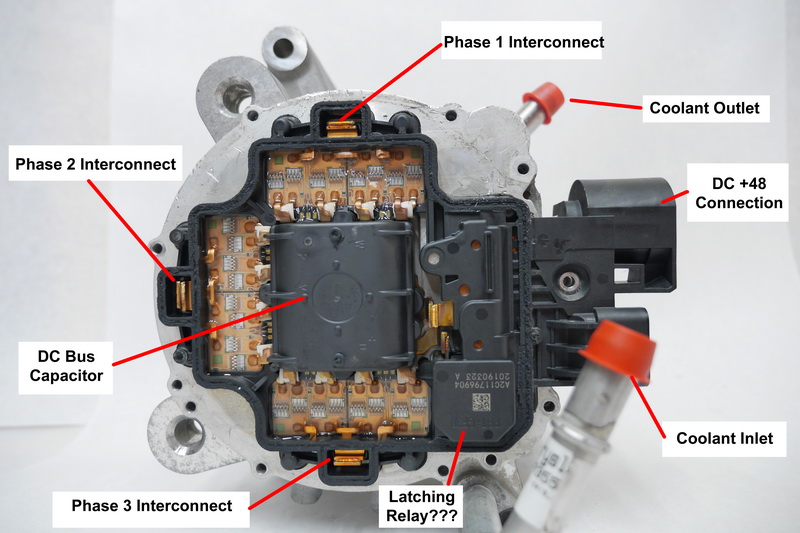
Jeep Wrangler 2019-2021 48V starter-generator power electronics
The power electronics of the 48V starter-generator for Jeep Wrangler 2019–2021 include: a three-phase bridge, a central direct current capacitor, and external interface equipment. The power electronics have three H-bridges, one for each phase. Each phase is welded to the engine controller buses.
If a pair of buses is disconnected from the controller, access to the control board, bearing assembly, and rotor is possible. The control board is covered by a plastic cover welded to the housing cover. It is not possible to reach the control board without destroying the plastic cover.
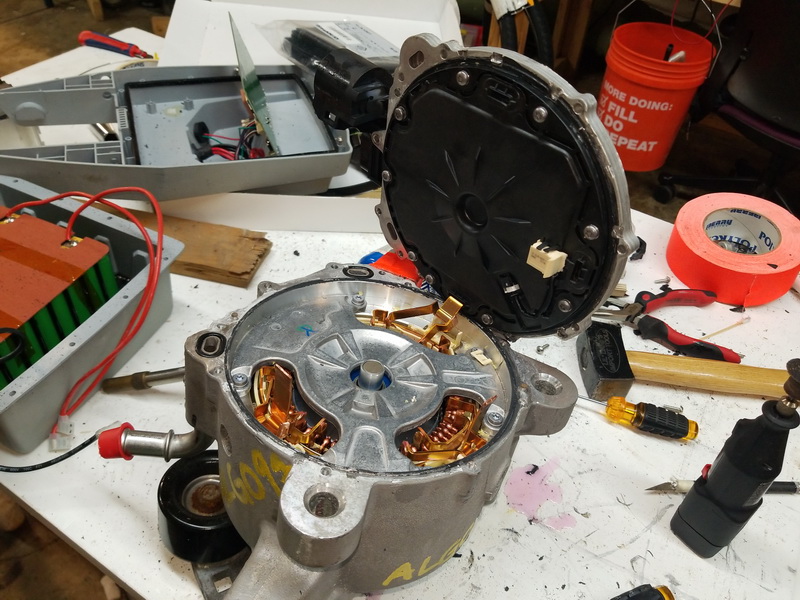
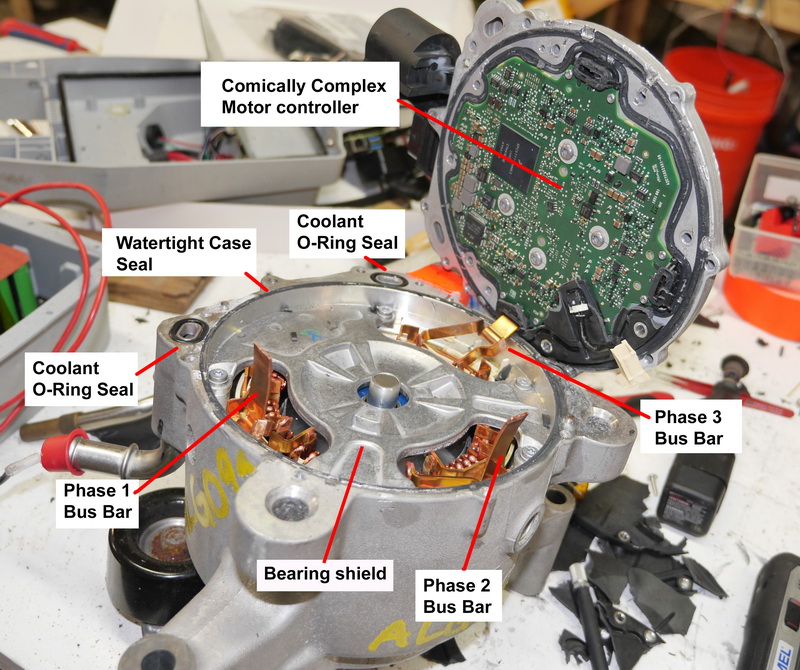
Conclusion
Despite the growing popularity of electric vehicles, automakers continue to improve internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles to reduce CO2 emissions and fuel consumption. The development of "mild hybrid" technologies with a 48V power system will create serious competition for more complex and expensive high-voltage power systems of plug-in hybrid (PHEV) vehicles and electric vehicles.
The materials of the article were used in writing the article https://transistor-man.com/everything_etorque.html



COMMENTS